The Sukanya Samriddhi Account or SSA was launched by the Government of India in 2015 to ensure a bright future for the girl children by facilitating their education and marriage expenses. The benefits of SSA are countless and offer a very attractive long term investment option including benefits under the income tax laws. However, there are much confusion and questions among the people about the SSA investment scheme and rules.
This article presents the SSA laws and rules in a simple and layman approach so that the confusion and questions among the investors get cleared.
Introduction
The Central Government launched the “Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao” scheme in January 2015 with the aim of bringing about an overall positive change in the mindsets of the people and to end discrimination against the girl child.
Through this scheme, the government would sensitize the citizens of this country towards the concerns of the girl child and women, thereby leading to the larger goal of gender equality.
Along with the "Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao" scheme, the government also launched the “Sukanya Samriddhi Account” programme.
Despite being a small savings scheme, the Sukanya Samriddhi Account has the potential to have a phenomenal impact on the lives and self-esteem of young girls in the country.
The scheme aims to ensure a bright future for girl children by facilitating their education and marriage expenses.
Relevant Legislation governing SSA
- The Government Savings Banks Act, 1873 now titled as the Government Savings Promotion Act, 1873.
- The Government Savings Promotion General Rules, 2018 and,
- The Sukanya Samriddhi Account Scheme, 2019. It came into effect from 12th December 2019 and overrides all the earlier rules notified so far prior to December 12, 2019.
Originally, the Sukanya Samridhi Account Rules, 2014 was released in December 2014. The 2014 rules were replaced by Sukanya Samridhi Account Rules, 2016. The rules were amended from time to time.
Presently, Sukanya Samriddhi Account Scheme, 2019 is in force.
Who can Open Sukanya Samriddhi Account
1. An account can be opened only by the guardian of a girl child.2. Account under this scheme can be opened only for a girl child whose age is less than 10 years as on the date of opening of the account.
3. A girl child can have only one account under this scheme.
4. The birth certificate of the girl child must be attached with the account opening form along with the KYC documents of the guardian.
5. In a family, an account under this scheme can be opened only for a maximum of two girl children. Exception is given for twins and triplets.
6. An account under this scheme can be opened for an adopted girl child also.
Note: The term 'family' is defined in the scheme as a unit consisting of a person, his spouse, and their children including adopted children.
7. An account shall be opened with a minimum contribution of Rs. 250.
8. An account under this scheme is opened by Form-1.
Periodic Contributions to an account
1. Any amount can be contributed to an account.
2. The minimum amount of deposit or contribution in an account in a financial year is Rs. 250.
3. Deposits must be made in multiples of Rs. 50.
4. The maximum amount of deposit or contribution in one account in a financial year is Rs. 1,50,000.
Note: If in any account in a financial year contribution of more than Rs. 1,50,000 is made, such excess contribution will not earn any interest and the same will be returned to the depositor without any interest.
5. Period of contribution: In an account, the contribution shall be required to be deposited for 15 years only from the date of opening of the account. Hence, an SSA is a 15-year term account.
6. Default (or dormant) account: If in any year, minimum contribution of Rs. 250 is not deposited in any account, the account will be considered as an account under default (or dormant account).
7. Regularization of a dormant account: A dormant account or an account under default can be regularized by paying a penalty of Rs. 50 for each year of default.
Along with the penalty, the depositor has to contribute the minimum deposit amount of Rs. 250 for each year of default.
If a dormant account is not regularized in the 15-year period, the balance in the account will continue to earn the same rate of interest as an active account earns till the closure of the account. There is no loss of interest in a dormant account.
Interest on Deposit
1. Rate of interest on SSA: The present rate of interest on a Sukanya Samriddhi Account is 8.4 percent compounded annually.The rate of interest is announced quarterly.
2. Time of credit of interest: The interest is credited in an account at the end of each financial year. Even in case of transfer of account interest will be credited once at the end of the financial year.
3. Calculation of interest: The interest is calculated on the outstanding balance of every calendar month. The lowest balance at the credit of an account between the close of the fifth day and the end of the month is taken as the outstanding balance for that month.
For example, if the balance as of 5th November is Rs. 10,000. On 10th November, a contribution of Rs. 5,000 is deposited into the SSA account. Interest will be computed on Rs. 10,000 for the month of November.
Assuming there are no further transactions in December, the outstanding monthly balance for computing interest for the month of December will be taken as Rs. 15,000.
In this case, Rs. 5,000 will not earn any interest for the month of November.
If the contribution is deposited on 4th November, instead of 10th November, then the outstanding monthly balance for computing interest for the month of November will be taken as Rs. 15,000 and not Rs. 10,000.
In this case, Rs. 5,000 will earn interest for the month of November.
Assuming that the amount is contributed to SSA from the depositor's savings account, where interest is given on a daily balance basis, one can earn a maximum amount of interest on depositing the contribution on the 5th of a month.
The depositor will earn interest up to 4th day in the savings account and also he will earn interest for the whole month in the SSA account.
Who can Operate an SSA account
It must be remembered that an account under the SSA scheme is opened for a minor girl child only by her guardian.Till the account holder or the minor girl child attains majority, the account shall be operated by her guardian only.
After the girl child attains majority (i.e. attains the age of 18 years), she should herself operate the account.
Premature Closure of an account
Accounts opened under the SSA scheme are meant for long term investments. Hence, premature closure is not allowed under normal circumstances.However, under certain special circumstances, premature closure of an account is allowed -
a) after the lock-in period
b) without any lock-in period.
a) An account opened under this scheme can be closed before maturity after a lock-in period of 5 years from the date of opening of the account in case of extreme compassionate grounds.
For example, life-threatening disease of the account holder or death of the guardian of the account holder is considered as extreme compassionate grounds.
b) An account opened under this scheme can be closed at any time before maturity in the event of the death of the girl child.
In this case, the account shall be closed immediately by an application in Form -2. The lock-in period of 5 years is not applicable in this situation.
In this case, interest on the balance in the account for the period between the date of death and the date of closure of account shall be paid at the rate of 4 percent, the rate of interest applicable to Post Office Savings Account.
Partial Withdrawal
1. When Partial Withdrawal is allowed: Partial withdrawal from an account under SSA scheme is allowed when the account holder (the girl child) -(i) has passed the tenth-standard, or
(ii) attains the age of 18 years
whichever is earlier.
2. Purpose of withdrawals: Amount from an account under the SSA scheme can be withdrawn before the maturity only for the purpose of higher education of the girl child.
3. Limit of amount: The maximum amount that can be withdrawn from an account under the SSA scheme is 50 percent of the balance in the account as at the end of the preceding financial year in which application for partial withdrawal is made.
For example, if an application for withdrawal from an account under the SSA scheme is made on January 3, 2020, then the outstanding balance as on 31.03.2019 will be considered for computing the 50 percent.
4. Applicable Form: The application for withdrawal from an account under the SSA scheme shall be made in Form-3.
5. Ceiling in withdrawal limit: The withdrawal from an account under the SSA scheme shall be made in one lump sum or in 5 annual installments.
6. Documentary evidence: Proper documentary evidence from the educational institution is required for withdrawals from an account under the SSA scheme. The amount of withdrawal will be limited to the fees and other charges as shown in the documentary evidence.
Closure of account on maturity
An account under the SSA scheme can be closed -(a) Upon completion of 21 years: An account opened under the SSA scheme matures on completion of 21 years from the date of opening of the account.
Many times it is misunderstood as the account shall mature on completion of 21 years of age of the girl child. Remember, it matures on completion of 21 years of the account.
If an account is opened when the age of the girl child is 10 years, the account will mature on completion of 21 years from the opening of the account and when the account will mature, the age of the girl child will be 31 years.
(b) Before completion of 21 years: An account opened under the SSA scheme can be closed before completion of 21 years on the marriage of the girl child after attaining the age of 18 years.
However, if she wishes, she may continue the account till the maturity of 21 years.
In case the account holder wishes to close the account on marriage then the same shall be made within one month before the date of the intended marriage or within three months after the date of marriage.
An application for closure of an account shall be made in Form-4.
Applicability of Government Savings Promotion General Rules, 2018
The Sukanya Samriddhi Account or SSA Scheme, 2019 provides that where no specific rule is made in this scheme then the provisions of Government Savings Promotion General Rules, 2018 shall apply to this scheme.Income Tax Benefits on an SSA Account
The income tax benefits or incentives on an SSA account is not a part of the Sukanya Samriddhi Account Scheme, 2019.The tax benefits are provided in the Income Tax Act, 1961.
An SSA account falls under Exempt-Exempt-Exempt (EEE) category. This means the contribution to an SSA account is exempt from tax, the interest income on an SSA account is exempt from tax and the withdrawal from an SSA account is also exempt from tax.
Tax deduction on Contribution to an SSA account
Contributions in a Sukanya Samriddhi Account (SSA) account are eligible for tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, 1961. The maximum amount of deduction that can be claimed under section 80C is Rs. 1,50,000. One can invest the entire limit of Rs. 1,50,000 in an SSA account and can claim a deduction of Rs. 1,50,000 from total income to reduce his tax liability.
The deduction can be claimed by the parent or the guardian of the girl child who has deposited the contribution into the SSA account.
Tax exemption on interest income on an SSA account
The annual interest income earned on an SSA account is exempt from income tax under section 10(11A) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. It means the interest income will not be included in computing the total income of the individual. The entire amount of interest income from an SSA account is tax-free.
Since the SSA interest income is tax-free, no tax is payable on the SSA interest income. Therefore, the present SSA rate of interest of 8.4 percent is the after-tax rate of tax.
On the contrary, the interest income from Fixed Deposits are not tax-free but are taxable. Hence, the rate of interest quoted for Fixed Deposits is a pre-tax rate of interest.
Suppose, the rate of interest on a Fixed Deposit is quoted as 8% compounded quarterly. It translates the coupon rate of interest to 8.24% per annum.
If a taxpayer compares the FD rate of interest of 8.24 percent with the SSA rate of interest of 8.4 percent, he is wrong. For an individual, who does not fall under any tax bracket, the comparison is correct but not for a person who falls in any tax bracket.
Even for an individual who falls in a 5 percent tax bracket, the after-tax rate of interest on FD comes to 7.8 percent which is far below the after-tax rate of interest of 8.4 percent on an SSA account.
For an Individual who pays tax @ 30 percent, the comparable FD interest rate falls to 5.8 percent.
In computing the tax effect, the surcharge and health and education cess ignored for the sake of simplicity.
How SSA interest rate does better than Fixed Deposit interest rate at different tax rates-
Rate of Tax
|
5%
|
20%
|
30%
|
After-tax rate of tax on Fixed Deposit
( 8% coupon rate) (in %)
|
7.8
|
6.6
|
5.8
|
After-tax rate of tax on SSA (in %)
|
8.4
|
8.4
|
8.4
|
It may be remembered that interest income from an SSA account is exempt income and needs to be reported in Income Tax Return or ITR in the Schedule-Exempt Income.
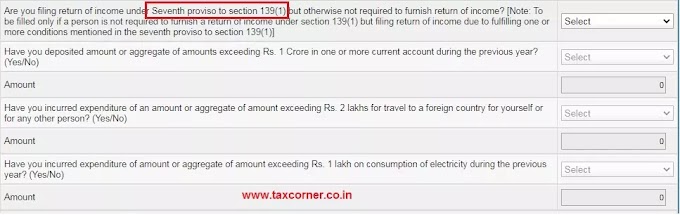
In ITR-1, the manner in which the exempt SSA interest needs to be reported is shown below-
In the 'Computation of Income and Tax Tab'. enter the SSA interest under the heading 'Exempt Income: For reporting purposes'.
No TDS on SSA interest
Since the interest income is exempt from income tax, there is no TDS on SSA interest irrespective of quantum of interest income on an SSA account in a financial year.
Tax exemption on withdrawal from an SSA account
There is no provision in the income tax Act which provides charging of income tax on the withdrawal from an SSA account. The withdrawal may be partial withdrawal or final withdrawal upon the maturity of the SSA account.
Hence, withdrawal from an SSA account is also free from income-tax.
Note: When the scheme was introduced in the Budget of 2014 (presented in July 2014), the only tax benefit available was the deduction u/s 80C for the contribution to the account opened under the scheme. The scheme was notified under section 80C(2)(viii) vide Notification number 9/2015 S.O.210 (E),F.No. 178/3/2015-ITA-I dated 21.012015. However, in Budget 2015, the interest income from an SSA account is made tax-exempt and the withdrawal from the account was made tax free. Such amendments were applied with retrospective effect from the assessment year 2015-16.
Appendix-1: Different Forms notified under the Sukanya Samriddhi Account Scheme, 2019 and their purposes
Form No.
|
Purpose
|
Form-1
|
Application for opening an account
|
Form-2
|
Application for premature closure of account
|
Form-3
|
Application for Withdrawal
|
Form-4
|
Application for closure of account
|
Download New Forms.
Appendix-2: Historic rate of interest on SSA scheme since 2014-15
|
Year
|
Rate of
interest (p.a.)
|
|
For FY 2014-15
|
9.1%
|
|
For FY 2015-16
|
9.2%
|
|
For Q-1 FY 2016-17 (Apr’16-Jun’16)
|
8.6%
|
|
For Q-2 FY 2016-17 (July’16-Sep’16)
|
8.6%
|
|
For Q-3 FY 2016-17 (Oct’16-Dec’16)
|
8.5%
|
|
For Q-4 FY 2016-17 (Jan’17-Mar’17)
|
8.5%
|
|
For Q-1 FY 2017-18 (Apr’17-Jun’17)
|
8.4%
|
|
For Q-2 FY 2017-18 (July’17-Sep’17)
|
8.3%
|
|
For Q-3 FY 2017-18 (Oct’17-Dec’17)
|
8.3%
|
|
For Q-4 FY 2017-18 (Jan’18-Mar’18)
|
8.1%
|
|
For Q-1 FY 2018-19 (Apr’18-Jun’18)
|
8.1%
|
|
For Q-2 FY 2018-19 (July’18-Sep’18)
|
8.1%
|
|
For Q-3 FY 2018-19 (Oct’18-Dec’18)
|
8.5%
|
|
For Q-4 FY 2018-19 (Jan’19-Mar’19)
|
8.5%
|
|
For Q-1 FY 2019-20 (Apr’19-Jun’19)
|
8.5%
|
|
For Q-2 FY 2019-20 (July’19-Sep’19)
|
8.4%
|
|
For Q-3 FY 2019-20 (Oct’19-Dec’19)
|
8.4%
|
|
For Q-4 FY 2019-20 (Jan’20-Mar’20)
|
8.4%
|
Read Also:
Get all latest content delivered straight to your inbox






0 Comments